In Sponsored Education
Bookmark
Supporting customers with chronic idiopathic urticaria
Managing symptoms associated with CIU to improve your customer’s quality of life
Chronic idiopathic urticaria (CIU) is a distressing skin condition that presents as hives on the skin lasting for more than six weeks, without any known cause.1 Symptoms can last for months, or even years, and can have a significant impact on your customer’s quality of life (QOL).1 Although many customers may be under the care of a healthcare professional (HCP) for their condition, when they present in pharmacy, you should be able to identify chronic idiopathic urticaria and support your customer with an appropriate treatment recommendation and self-care advice.
After reading this module, you will be able to:
Understand what CIU is and the impact it can have on sufferers both physically and mentally
Recognise how Histahive is used to relieve symptoms of CIU
Offer your customer self-care advice to help relieve and prevent worsening of symptoms
Identifying urticaria
As mentioned in the video, urticaria presents as red, raised patches on the skin that can affect any area of the body and tend to be widely distributed.1,2
Although many customers may know about their condition, it is important that you can differentiate CIU from other dermatological conditions in order to correctly identify it.
Look at the images below of some dermatological conditions that may present in the pharmacy and think about which one of these could be urticaria. Consider how the characteristics of each condition differ to urticaria.
After considering each potential diagnosis, click on the image flashcard to learn more.1,4
Eczema
Eczema causes a rash that may be itchy, red, dry and scaly. Sometimes the yellow or white scaly patches flake off. However, the affected area could also be itchy, greasy and oily.

Psoriasis
Psoriasis causes scaly, silvery, sharply defined skin plaques. They usually occur on the scalp, elbows, knees and lower back.

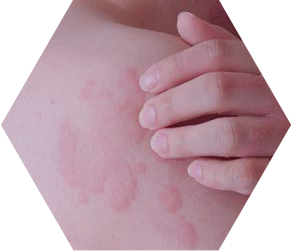
Urticaria (hives)
Urticaria causes itchy, raised, red wheals that typically occur after exposure to an allergen. However, in cases of CIU, there is no identifiable cause. They can affect any part of the body and are widely distributed.

Shingles
Shingles causes a painful rash that appears are blotches on one side of the body only. It usually presents on the chest and abdomen but can appear anywhere.

Chickenpox
Chickenpox causes clusters of itchy, red or brown fluid-filled blisters all over the body. It is usually accompanied by other symptoms including fever.

Acne
Acne breakouts can often affect the face, neck and back. They appear as ‘spots’ and are more common during puberty.
NOTE: Remember, these conditions can appear differently on different skin tones; in particular, on darker skin tones, they may be harder to see or appear less red.3

